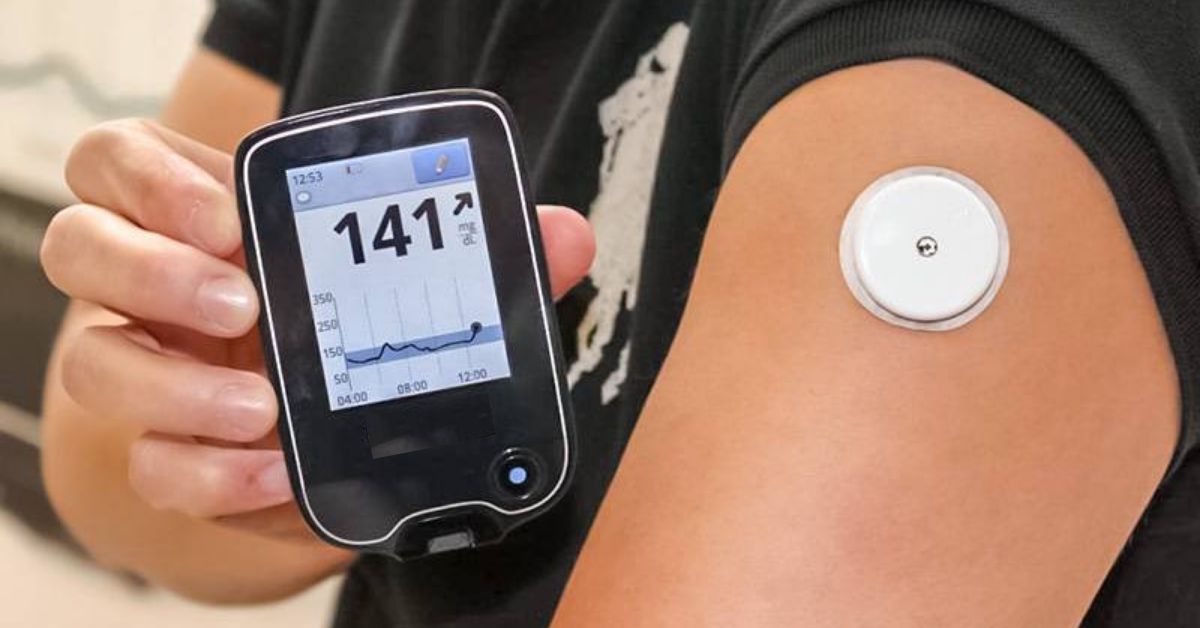
Glucose (Blood Sugar) Monitoring
Checking blood glucose levels regularly helps to ensure they remain within a healthy target range. High blood sugars can cause severe damage to the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, feet, and eyes over time. Low blood glucose impairs the ability to think and function normally. It's essential to monitor blood glucose levels both over time (A1C testing) and at specific times throughout the day (meter testing).
All About Blood Glucose
A1c Testing

A1c
Information Guide
The hemoglobin A1c test measures the average blood glucose level over the past three months (24 hours a day, 7 days a week) and differs from blood glucose checks performed daily with a meter.
At least two A1c tests are recommended every year (at a minimum) in addition to daily blood glucose monitoring.
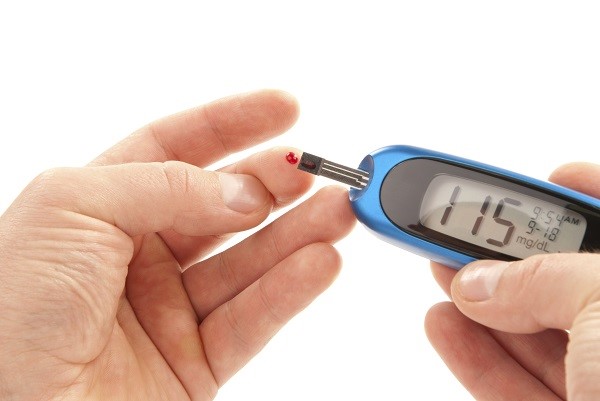
Blood Glucose (Blood Sugar) Meter Testing
-
Checking blood glucose using a meter shows your blood sugar level at any given time
-
Discuss with your care team how often you should be testing your blood glucose
Checking blood sugar throughout the day
Testing glucose levels at the same time each day allows you to track patterns. For people who receive multiple daily insulin injections or use an insulin pump, it's generally recommended to test before meals and snacks, occasionally two hours after the first bite of a meal, at bedtime, before exercising, when low glucose is suspected, after treating a low, and before critical tasks such as driving.
Hypoglycemia
(Low Blood Glucose)
Hypoglycemia is defined as blood glucose levels that are less than usual (usually below 70 milligrams per deciliter). Symptoms include excessive hunger, shakiness, sweating, dizziness, lightheadedness, pale skin, and/or confusion. Left untreated, hypoglycemia may lead to unconsciousness.
Hyperglycemia
(High Blood Glucose)
Hyperglycemia is defined as blood glucose levels above the target range set by your care team. In general, it’s when glucose is above 180 mg/dL consistently. Symptoms include excessive thirst and/or urination.
Recording blood glucose results is important
Testing your blood sugar regularly is an integral part of diabetes self-management because it puts you in charge. Whether utilizing a smartphone app or a paper log, recording and sharing the results with your care team provides them with an overall picture of your body's response to your diabetes care plan. Download our printable blood glucose logs.
Blood Glucose Log
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM)